 |
 |
|
| Department of Public Health & Preventive Medicine: |
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS 1. What is Japanese encephalitis? Japanese encephalitis (JE) is a potentially severe viral zoonotic disease caused by the Japanese Encephalitis(B) virus .It is an arbovirus belongs to family Flaviviridae, closely related to West Nile, St .Louis & Kunjin viruses. 2. What are the signs and symptoms of Japanese Encephalitis? Most people who are infected develop mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. In people who develop severe disease, initial symptoms include fever, chills, headache, fatigue, nausea and vomiting. The disease can progress to inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) and is often accompanied by seizures. Coma and paralysis occur in some cases. The course of the disease can be conveniently divided into 3 stages: A) Prodromal stage B) Acute encephalitic stage C) Late convalescent stage Prodromal stage: General malaise, abrupt onset of acute fever, head ache often accompanied with vomiting, ranges from 1 to14 days (average of 1 – 3 days). Acute encephalitic stage: Continuous fever (100 to 107° F), Stiff Neck, Convulsions, Altered Sensorium, Focal CNS signs, Delirium, Stupor and finally progressing to Coma. Most death occurs in this stage. Late convalescent stage: Temperature returns to normal , Neurological signs stationary or tend to improve and residual neurological deficit are common. 3. How Japanese Encephalitis is transmitted? Transmitted by certain species of Cx.vishnui subgroup of mosquitoes like Cx. Vishnui, Cx.pseudovishnui, and Cx.tritaeniorhynchus. The migratory birds carry the virus in them which is transmitted to man through the amplifier host (pig) by the mosquitoes. Man is the accidental host  Mosquitoes become infected by feeding on domestic pigs and wild birds infected with the Japanese encephalitis virus. Infected mosquitoes then transmit the Japanese encephalitis virus to humans and animals during the feeding process. The Japanese encephalitis virus is amplified in the blood systems of domestic pigs and wild birds. 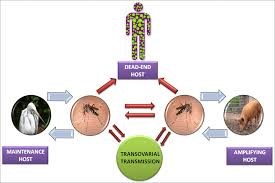 4. Where do the Japanese encephalitis vector mosquitoes breed? They breed mainly in Paddy fields. 5. Could you get the Japanese encephalitis from another person? No, Japanese encephalitis virus is NOT transmitted from person-to-person. For example, you cannot get the virus from touching or kissing a person who has the disease, or from a health care worker who has treated someone with the disease. 6. Where does Japanese encephalitis occur? JE usually occurs in rural or agricultural areas, often associated with rice farming. Transmission is seasonal, and human disease usually peaks in the months of July and October. 7. How soon do people get sick after being bitten by an infected mosquito? It takes 5 to 15 days after the bite of an infected mosquito to develop symptoms. 8. How is Japanese encephalitis diagnosed? Diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical signs and symptoms and specialized laboratory tests of blood or spinal fluid. These tests typically detect antibodies that the immune system makes against the viral infection. List of diagnostic facilities for Japanese Encephalitis in Tamil Nadu
9. What is the treatment for Japanese encephalitis? There is no specific treatment. Severe illnesses are treated by supportive therapy which may include hospitalization, respiratory support, and intravenous fluids. 10. Is there a vaccine for Japanese encephalitis? Yes. Initially Mouse brain killed vaccine was given to children in Perambalur district of Tamil Nadu and had shown good results. With the Government of India support SA-14-14-2 type of JE vaccine is given to the children in the age group of 1-15 years in 13 JE endemic districts viz. Tiruvallur, Tiruvannamalai, Villupuram, Cuddalore, Perambalur, Ariyalur, Thiruvarur, Thanjavur, Pudukottai, Tiruchirapalli, Madurai, Virudhunagar and Karur as a single dose during campaign mode. Later, the children in these districts are given 2 doses of JE Vaccine in the age of 9 months and 16- 24 months. JE vaccination programme was conducted in a campaign mode in the above districts from 2007 onwards upto 2014 and later included under Routine Immunisation Programme. 11. Who should get Japanese encephalitis vaccine? JE vaccine is recommended for travelers who plan to spend at least 1 month in endemic areas during the JE virus transmission season. Vaccine should also be considered for the following:
12. How to eliminate the breeding of mosquitoes?
JE Cases and Deaths in Tamil Nadu 2012-2016
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home | Malaria | Dengue | Chikungunya Fever | Japanese Encephalitis | Filaria | Leprosy | Notifiable Diseases | |