- Abrupt onset of high fever
- Severe frontal headache
- Pain behind the eyes which worsens with eye movement
- Muscle and joint pains
- Measles-like rash over chest and upper limbs
- Nausea and vomiting
Signs & Symptoms of Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever and Shock Syndrome
- Symptoms similar to dengue fever
- Severe continuous stomach pains
- Skin becomes pale, cold or clammy
- Bleeding from nose, mouth & gums and skin rashes
- Frequent vomiting with or without blood
- Sleepiness and restlessness
- Patient feels thirsty and mouth becomes dry
- Rapid weak pulse
- Difficulty in breathing
Transmission Cycle of Dengue
| Dengue Cases and Deaths in Tamil Nadu 2013 - 2017 |
| Year |
Cases |
Deaths |
| 2013 |
6122 |
0 |
| 2014 |
2804 |
3 |
| 2015 |
4535 |
12 |
| 2016 |
2531 |
5 |
| 2017 (Upto-5.3.17) |
1002 |
1 |
Magnitude of the Problem
Period of Communicability
Infected person with Dengue becomes infective to mosquitoes 6 to 12 hours before the onset of the disease and remains so upto 3 to 5 days.
Age & Sex Group Affected
- All age groups & both sexes are affected
- Deaths are more in children during DHF outbreak
Vector of Dengue/Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever
- Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus are the vector of dengue / dengue haemorrhagic fever.
- It is a small, black mosquito with white stripes and is approximately 5 mm in size.
- It takes about 7 to 8 days to develop the virus in its body and transmit the disease.
Feeding Habit
- Day biter
- Mainly feeds on human beings in domestic and peridomestic situations
- Bites repeatedly
Resting Habit
- Rests in the domestic and peridomestic situations
- Rests in the dark corners of the houses, on hanging objects like clothes,umbrella, etc. or under the furniture
Breeding Habits
- Aedes aegypti mosquito breeds in any type of manmade containers or storage containers having even a small quantity of water
- Eggs of Aedes aegypti can live without water for more than one year
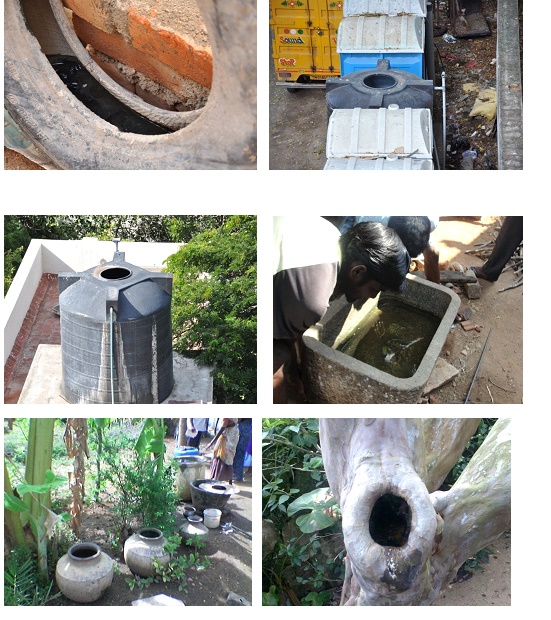
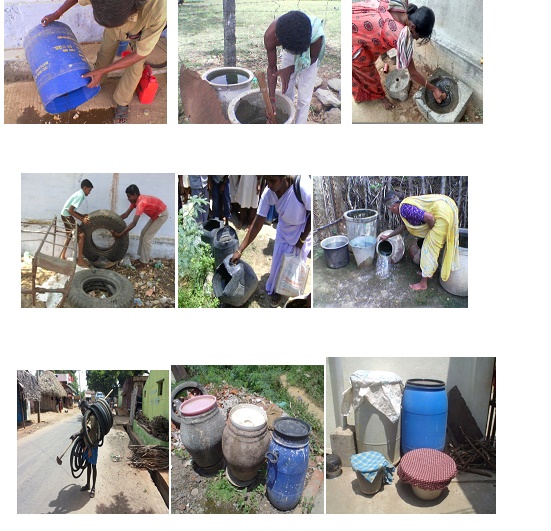
Common Breeding Places
Coconut shells, Drums, Jars, Pots, Buckets, Flower vases, Unused Grinding Stones, Plant saucers, Tanks, Cisterns, Bottles, Tins, Tyres, Roof gutters, Refrigerator drip pans, Cement blocks, Cemetery urns, Bamboo stumps, Desert coolers, Tree holes and many more places where rainwater is collected.
Control of Dengue Fever
Treatment of Dengue & DHF
- No drug or vaccine is available for the treatment of Dengue/DHF
- There is no specific medication for treatment of a dengue infection. Persons who think they have dengue should use analgesics (pain relievers) with paracetamol and avoid those containing aspirin.
- They should also rest, drink plenty of fluids and consult a physician.
- Early reporting of the suspected dengue fever
- Management of dengue fever is symptomatic & supportive
- In dengue shock syndrome, the following treatment is recommended
- Replacement of plasma losses
- Correction of electrolyte and metabolic disturbances
- Blood transfusion
- The control of Aedes aegypti mosquito is the only method of choice
- With early detection and proper case management and symptomatic treatment, mortality
can be reduced substantially
- Prevention is better than cure
Indian System of Medicine-Siddha Medicine
Treat and prevent Dengue fever with traditional Siddha Medicine
- Papaya Leaf Juic
Fresh Papaya leaves (excluding veins) should be mixed with a little cold water and ground and filtered. Consume 10 ml four times a day. Fever will subside on consumption for five days. Even after recovery from fever this may be continued for another two days. Papaya leaf juice is a traditional home made natural medicine.
- Malai Vembu Leaf (Hill Neem) Juice
Fresh Malaivembu leaves should be mixed with a little cold water and ground and filtered. Consume 10 ml two to three times a day. Fever will subside on consumption for five days. Even after recovery from fever this may be continued for another two days. Malaivembu leaf juice is a traditional home made natural medicine.
- Nilavembu Kudineer
Boil 10 grams of Nilavembu Kudineer Powder in 100 ml of water until it gets reduced to half and consume 50 ml two times per day in the morning and evening. Prepare the Nilavembu Kudineer freshly for each dose. Fever will subside on consumption for five days. Even after recovery from fever this may be continued for another two days. Nilavembu Kudineer powder is available in all Siddha wings in Government Hospitals and Primary Health Centres free of cost.
Vector Control Measures
1. Personal Prophylactic Measures
- Use of mosquito repellent creams, liquids, coils, mats etc.
- Wearing of full sleeve shirts and full pants with socks
- Use of bed nets for sleeping infants and young children during day time to prevent mosquito bite
2. Biological Control
- Use of larvivorous fishes in ornamental tanks, fountains, etc.
3. Chemical Control
- Use of chemical larvicides like Temephos 50% EC in big water holdings
- Aerosol space spray during day time in and around the houses, market places, large campuses and buildings using Pyrethrum 2% Extract.
4. Environmental Management & Source Reduction Methods
- Identification and destruction of mosquito breeding sources
- Management of roof tops, porticos and sunshades
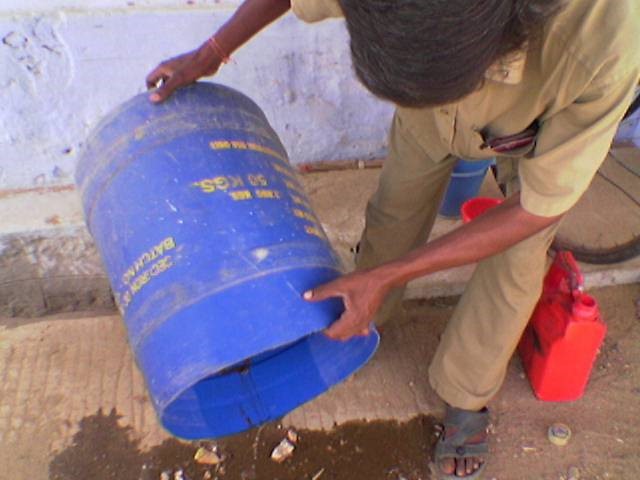
- The water storing containers should be scrubbed and washed with bleaching powder every week.
- They should be properly covered with a cloth or sheet so as to prevent mosquito breeding in the water containers.
- Reliable water supply
- Observation of weekly dry day
5. Health Education
- Impart knowledge to common people regarding the disease and vector through various media sources like T.V., Radio, Cinema slides, etc.
6. Dengue Fever Mobile App in Tamil
- The Dengue Fever Mobile App can be downloaded from Google Play Store.
- Dengue Fever Tamil App provides complete pictorial information about the sources where Aedes mosquitoes breed along with an exhaustive Frequently Asked Questions.
- Information on effective siddha treatment is made available.
- To get better understanding, an audio Jingle and videos by celebrities are also included. All materials are given in Tamil.
- User can directly dial 108, 104 and 24 X 7 Public Health Control Room through this App.
7. Community Participation
- Sensitilizing and involving the community for detection of Aedes breeding places and their elimination
Do's and Don'ts
- Remove water from coolers and other small containers at least once in a week
- Use aerosol during day time to prevent the bites of mosquitoes
- Do not wear clothes that expose arms and legs
- Children should not be allowed to play in shorts and half sleeved clothes
- Use mosquito nets or mosquito repellents while sleeping during day time
List of Sentinel Surveillance Hospitals (30) for Dengue and Chikungunya
1 Kanyakumari Medical College, Kanyakumari
2 Tirunelveli Medical College, Tirunelveli
3 Thoothukudi Medical College
4 Thanjavur Medical College
5 Govt. Mohan Kumaramangalam Medical College, Salem
6 Coimbatore Medical College, Coimbatore
7 K.A.P.Viswanathan Medical College, Trichy
8 Theni Medical College, Theni
9 Chengalpattu Medical College, Chengalpattu
10 Madurai Medical College, Madurai
11 Vellore Medical College, Vellore
12 Madras Medical College, Chennai
13 Institute of Vector Control and Zoonoses, Hosur
14 Dharmapuri Medical College- Dharmapuri
15 Villupuram Medical College-Villupuram
16 District Head quarters Hospital, Ramanand
17 Thiruvarur Medical College- Thiruvarur
18 District Hospital, Cuddalore
19 Zonal Laboratory, Vellore
20 Zonal Laboratory, Cuddalore
21 Zonal Laboratory, Trichy
22 Zonal Laboratory, Dindugal
23 Zonal Laboratory, Tanjavur
24 Zonal Laboratory, Virudhunagar
25 Zonal Laboratory, Thirunelveli
26 Zonal Laboratory, Salem
27 Zonal Laboratory, Coimbatore
28 Stanley Medical College Hospital, Chennai
29 Communicable Disease Hospital, Chennai
30 Kilpaulk Medical College Hospital, Chennai
Apex Referral Laboratories (1)
- King�s Institute of Preventive Medicine, Chennai.