 |
 |
|
| Department of Public Health & Preventive Medicine: |
|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. What is Malaria ? Malaria is a parasitic disease caused by the Genus Plasmodium and spread by Anopheles mosquitoes. 2 .What are the symptoms of Malaria ? Fever, Headache, Bodyache, Rigor, Chill and Vomiting. 3 .How does malaria spread ? Malaria is spread by an infected female anopheles mosquito which breeds in fresh water collections like OHTs, cisterns, wells, sumps etc. There is no direct transmission from the infected person to the healthy person.  4. Is there different type of malaria ? Yes.There are 4 types of malaria namely Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium malaria and Plasmodium ovale. 5. Do all these are prevalent in Tamil Nadu ? No. P. vivax and P. falciparum are prevalent in Tamil Nadu and P. vivax Malaria is more common. 6. What are the different types of vector mosquitoes ? There are 3 different types of vector mosquitoes. Anopheles stephensi, Urban vector; An.culicifacies, Rural vector; An. fluviatilis, Foot hill area vector. 7. How to eliminate the breeding of mosquitoes? Proper sealing of Over Head Tanks, wells and covering all water containers preventing mosquitoes from laying eggs and thereby preventing the mosquito breeding. 8. Will Malaria cause death ? Untreated P. falciparum may cause severe complications leading to death. 9. Is there a vaccine for Malaria ? No. 10. How does a person know that he is suffering from malaria ? Any person having fever and headache should be suspected as a malaria case and his blood should be examined for confirming the same. 11. Is there any specific treatment for Malaria ? Yes. After examining the blood-smear, if the person is found positive for malaria, radical treatment with Chloroquine and Primaquine should be administered as per the malaria drug schedule of National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme, Delhi. MALARIA TREATMENT SCHEDULE (As per NVBDCP Drug Policy - 2013)
Dosage Chart for Treatment of P.vivax Malaria {CQ - Chloroquine, PQ - Primaquine Note: Chloroquine 250 mg tablet is having 150 mg base. Do not give primaquine to pregnant woman, infants and G6PD deficiency cases. 14 days regimen of Radical Treatment should be given under supervision Dosage Chart for Treatment of P.falciparum Malaria with ACT-SP {Artesunate (AS), Sulfadoxine Pyremethamine (SP)} & Primaquine (PQ)
Note: Do not give primaquine to pregnant woman, infants and G6PD deficiency cases 3 days regimen of Radical Treatment should be given under supervision Treatment of uncomplicated P.falciparum cases in pregnancy: 1st Trimester: Quinine salt 10 mg/kg 3 times daily for 7 days. Quinine may induce hypoglycemis, pregnant woman should not start taking quinine on an empty stomach and should eat regularly, while on quininetreatment 2nd & 3rd Trimester: ACT as per dosage given above (without Primaquine). Dosage Chart for Treatment of mixed (vivax & falciparum) Infection Malaria with ACT-SP
Note: Do not give primaquine to pregnant woman, infants and G6PD deficiency cases 14 days regimen of Radical Treatment should be given under supervision 12. How to control malaria?
Treatment for malaria is free in all Government Hospitals, Primary Health Centres and Malaria Clinics 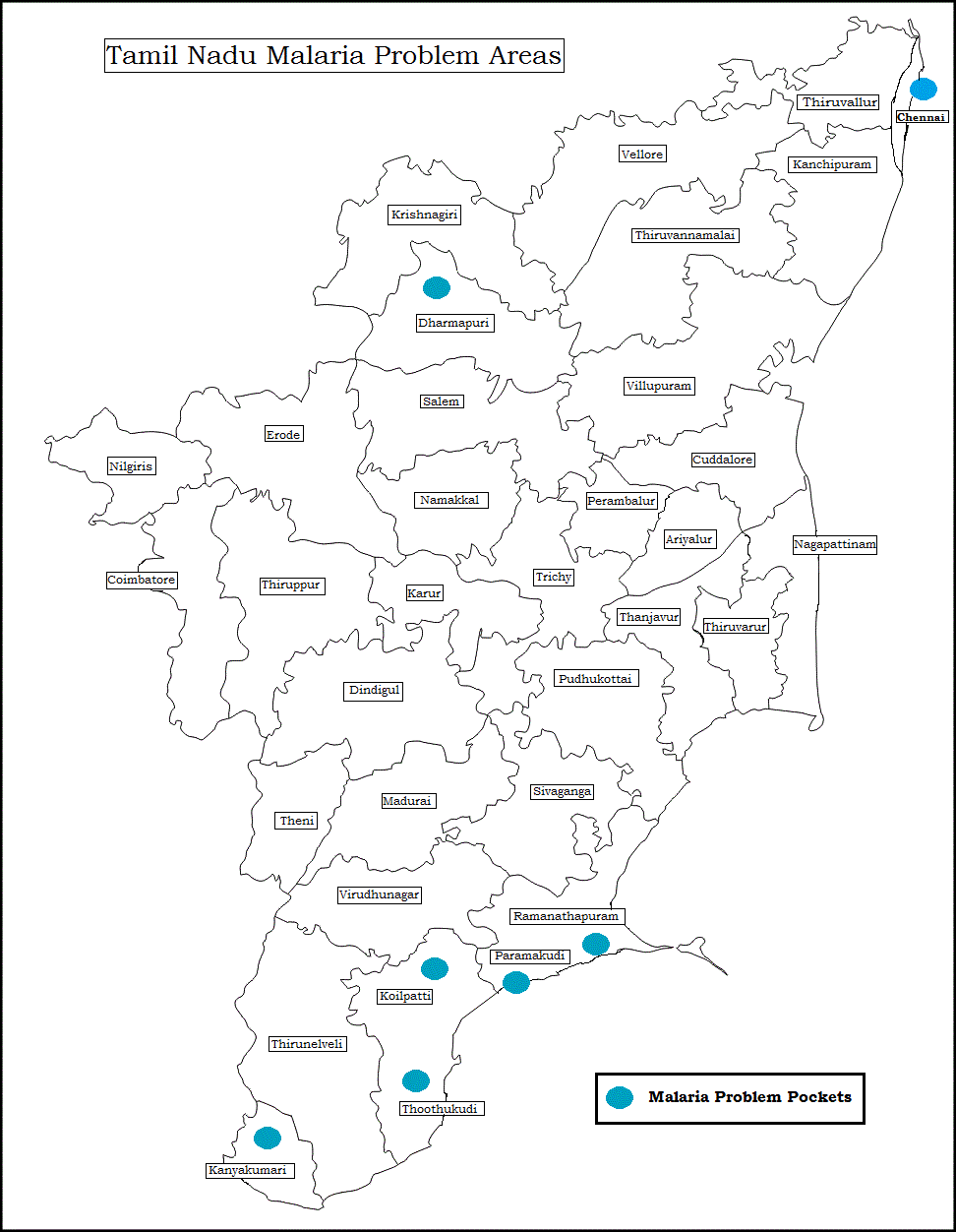 MALARIA INCIDENCE RURAL AND URBAN AREAS OF TAMIL NADU 2010 - 2017
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||